Mobile Snake Game
This was my second project in Unity. This project was also part of the IVGC (Introduction to Video Games Creation) course. This was the first time I was creating a game for the android platform.
I learned plenty of new concepts like touch inputs handling, designing the UI to fit properly on different sizes of mobile screen, etc.
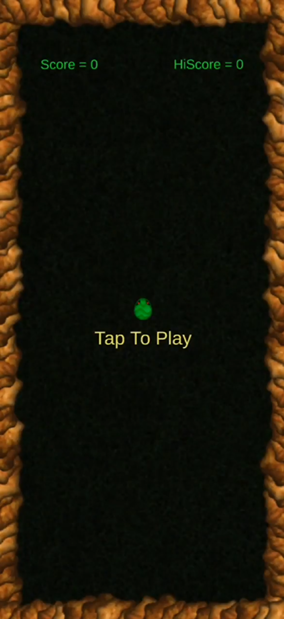
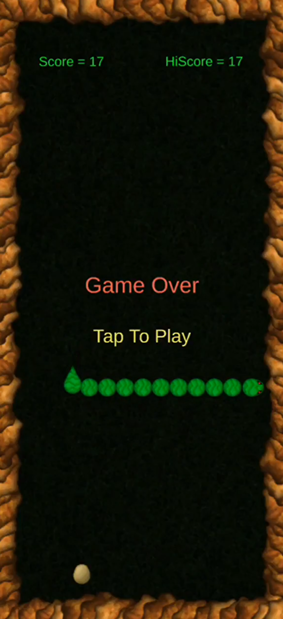
This is just a simple snake game that eats white eggs, to proceed to next level the snake needs to eat a golden egg. If the snake collides with itself or the walls, then the game ends with a ‘Game Over’ text.
Gameplay Video
What I Learned
- Singleton Pattern
- Object Instantiation and Prefabs
- Event Handling (C# Events)
- Touch Input/Swipe Detection
- Game State Mangement
- Movement and Collision Handling
- List Management
- Dynamic Object Movement
- Audio Management
- Sprite Manipulation
- Randomization
- Memory Management
- Game Over Logic and Restart
How I Implemented these Concepts
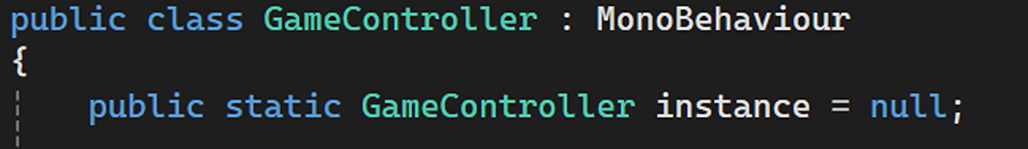
Singleton Pattern
Used to ensure there is only one instance of GameController throughout the game.
Object Instantiation and Prefabs
Instantiating prefabs at runtime for game objects like body parts, eggs, spikes, and rocks. GameController.cs:
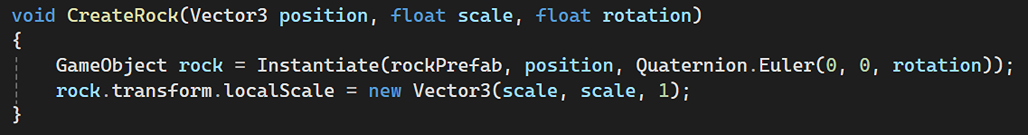
SnakeHead.cs does the same thing, instantiate the snake body parts at runtime.
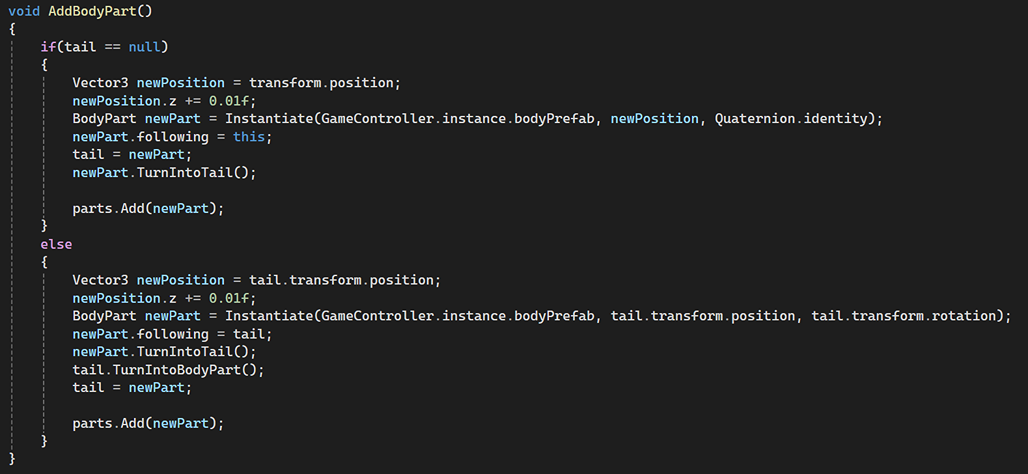
Event Handling (C# Events)
Using C# events to handle player input for swipe actions. SwipeControls.cs:
![]()
Touch Input/Swipe Detection
Detecting and handling user swipes (up, down, left, right) on a touch screen. SwipeControls.cs:
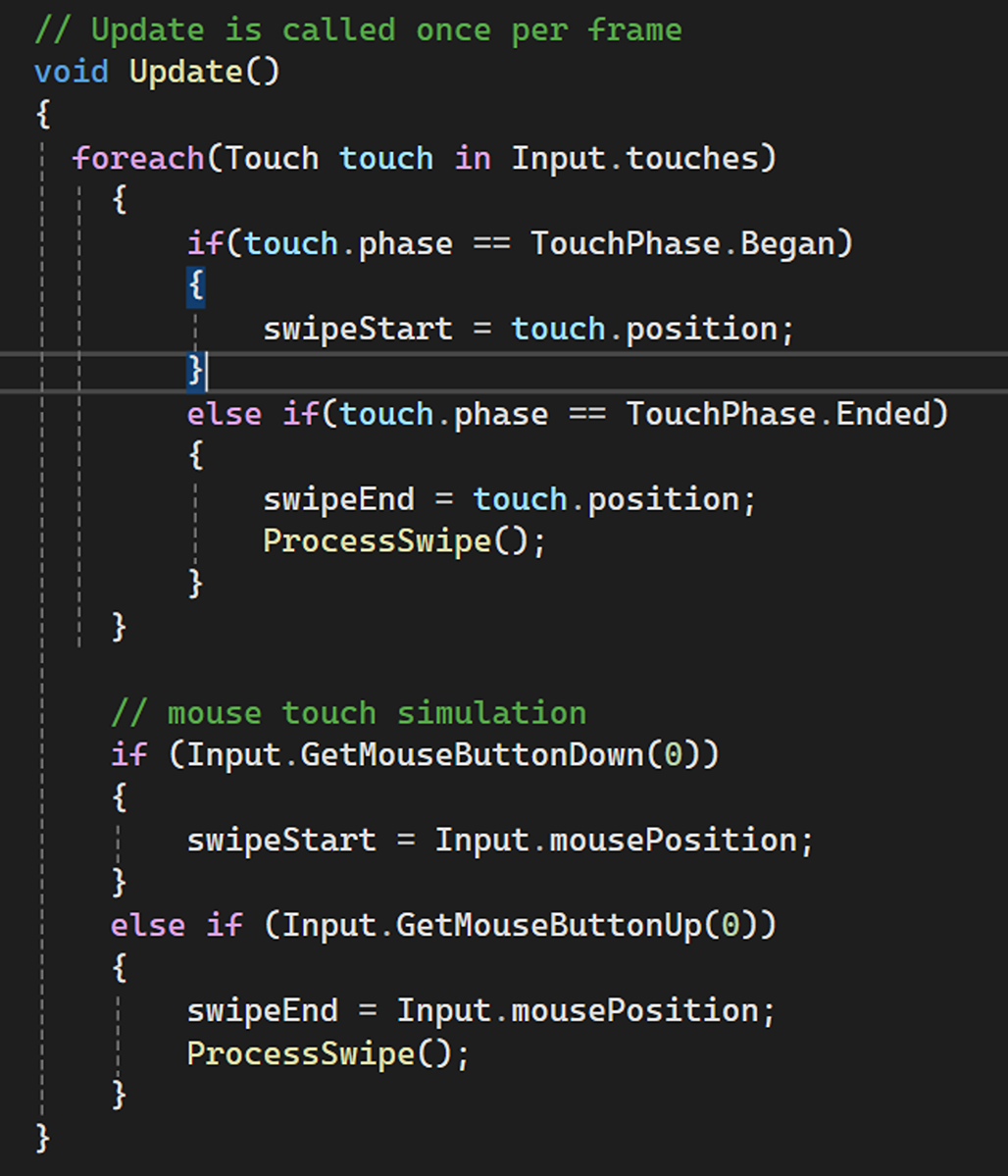
Game State Management
Managing different game states such as “waiting to play,” “game over,” and “in game,” while updating UI elements accordingly. GameController.cs: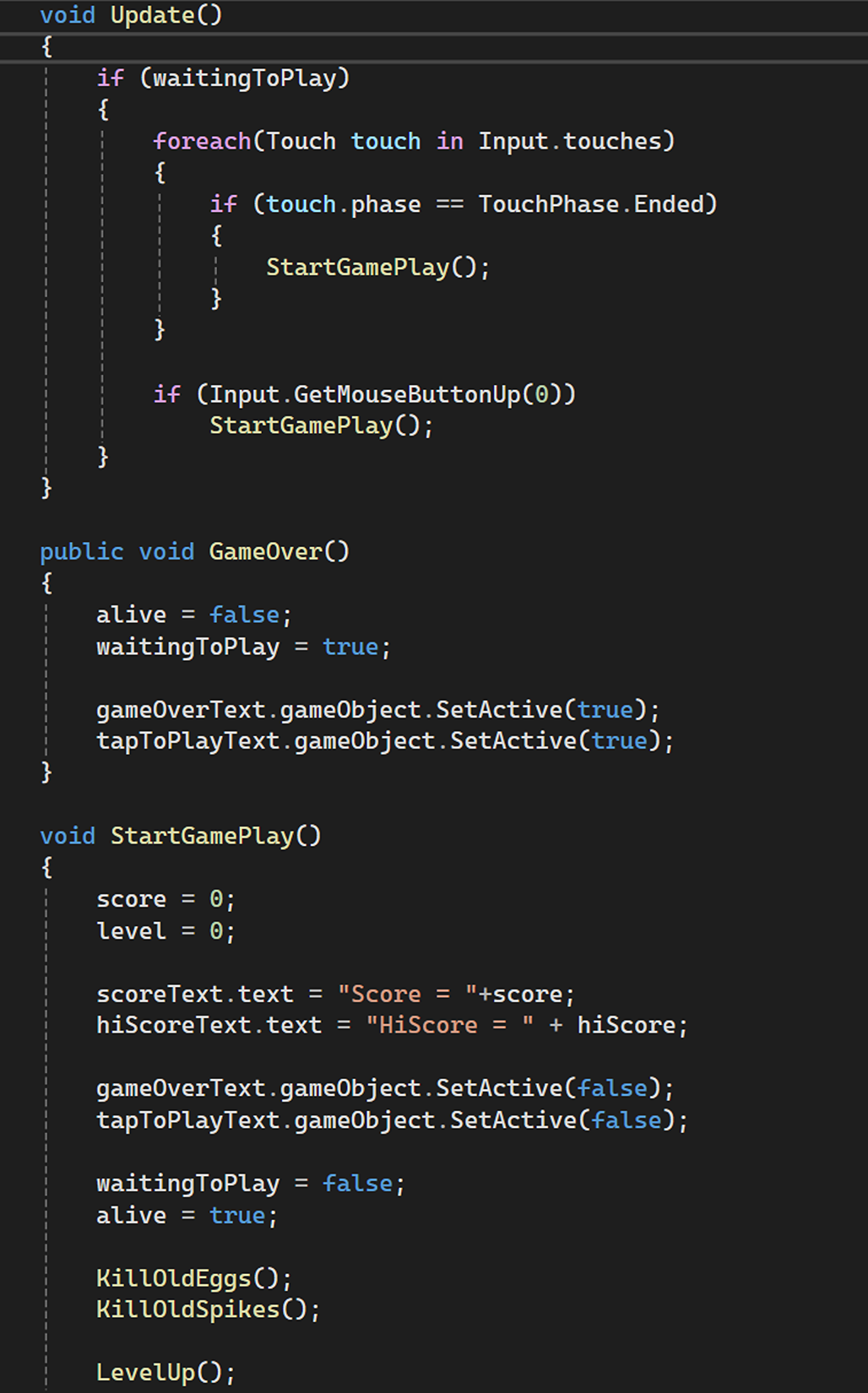
Movement and Collision Handling
Implementing movement logic (including swipe controls) and collision detection (for eggs, obstacles, and spikes).
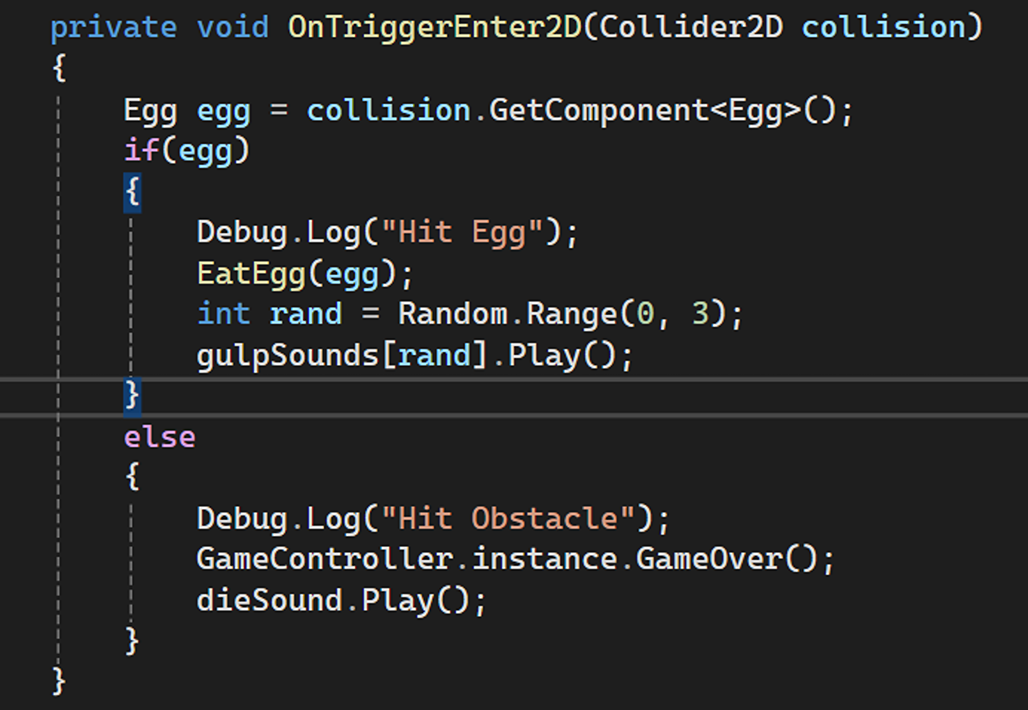
Movement Handling in the BodyPart.cs:
List Management
Using lists to manage dynamic objects like the snake’s body parts, eggs, and spikes. GameController.cs: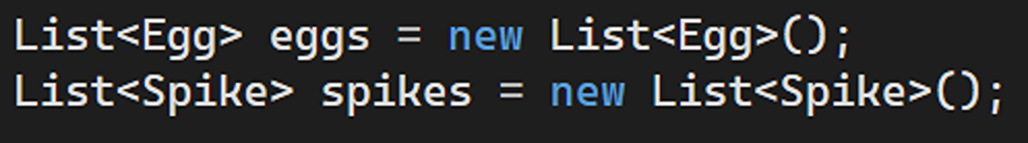
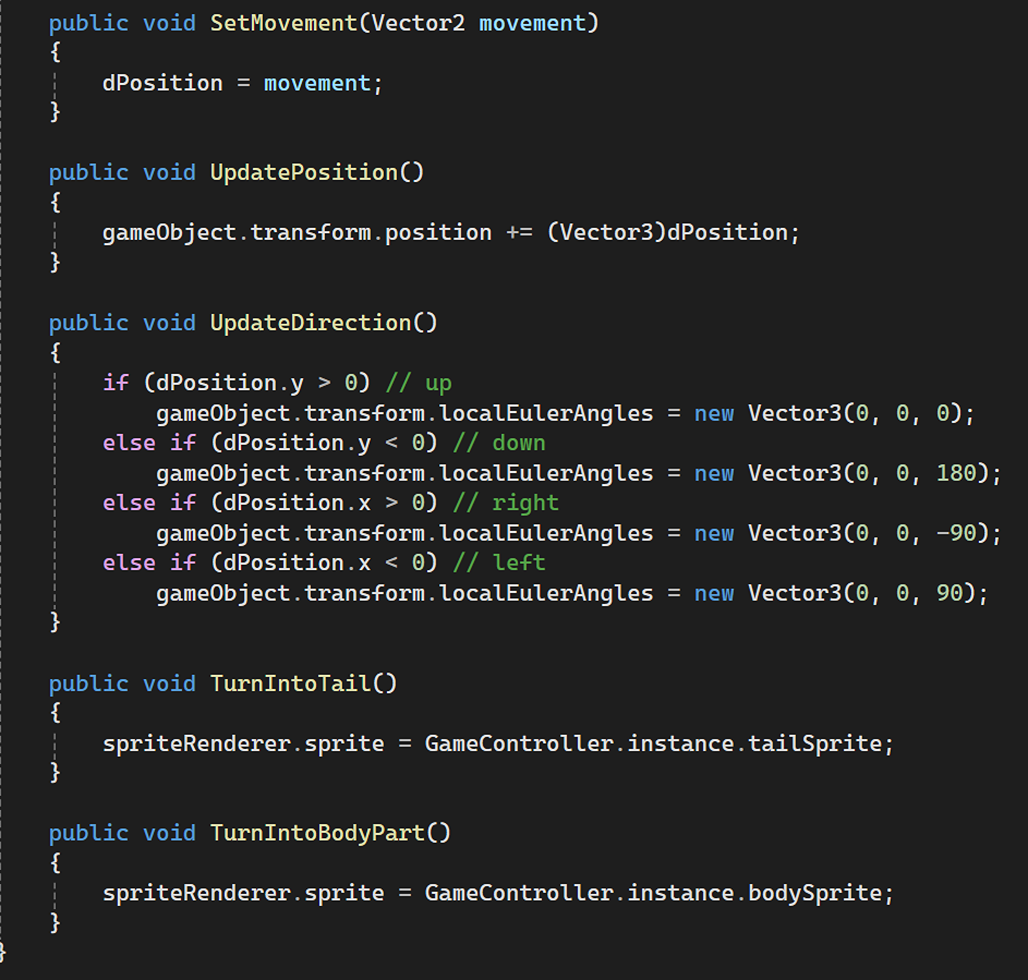
Dynamic Object Movement
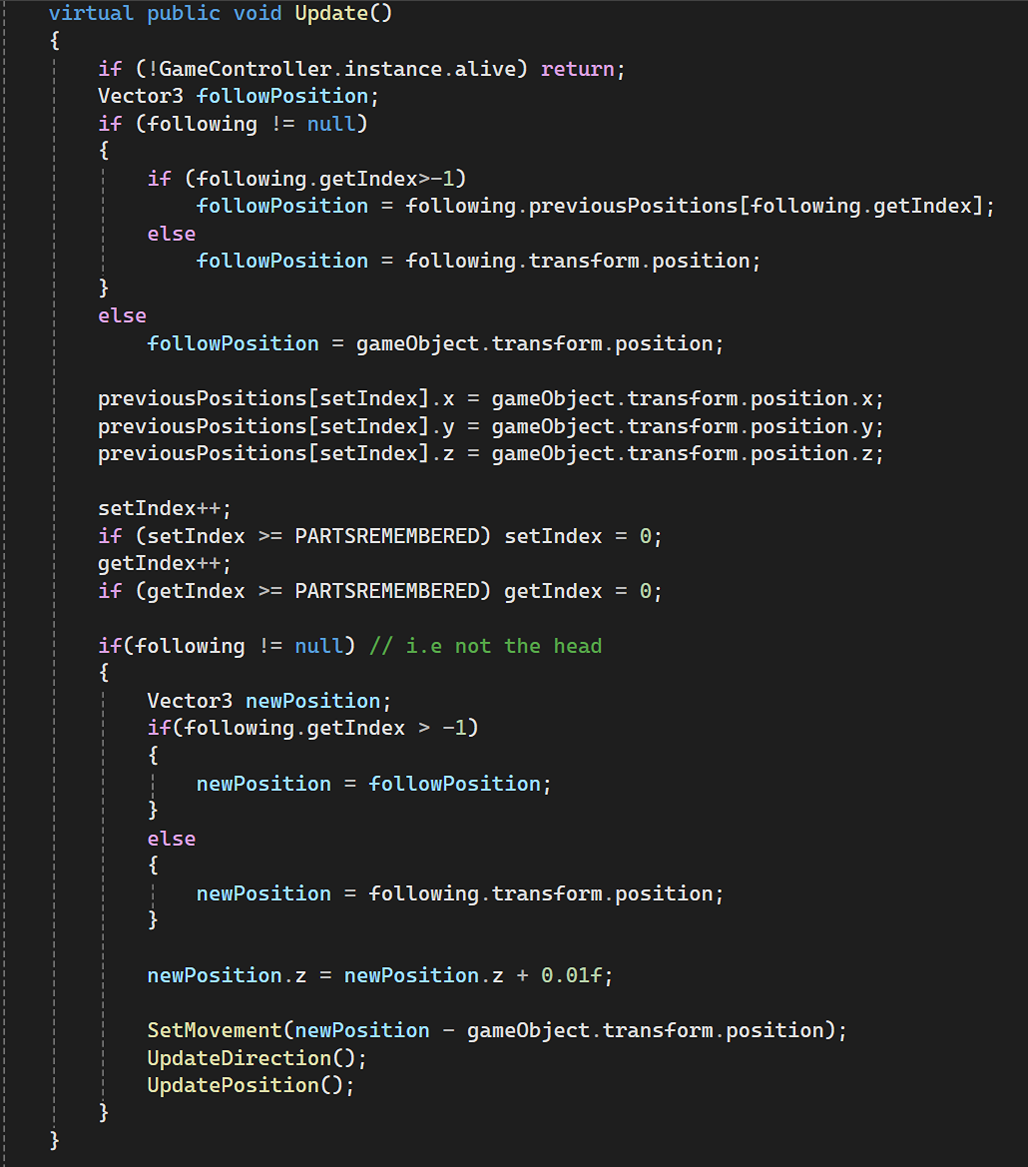
Managing smooth movement of dynamic objects like the snake’s body parts, ensuring each part follows the previous part.
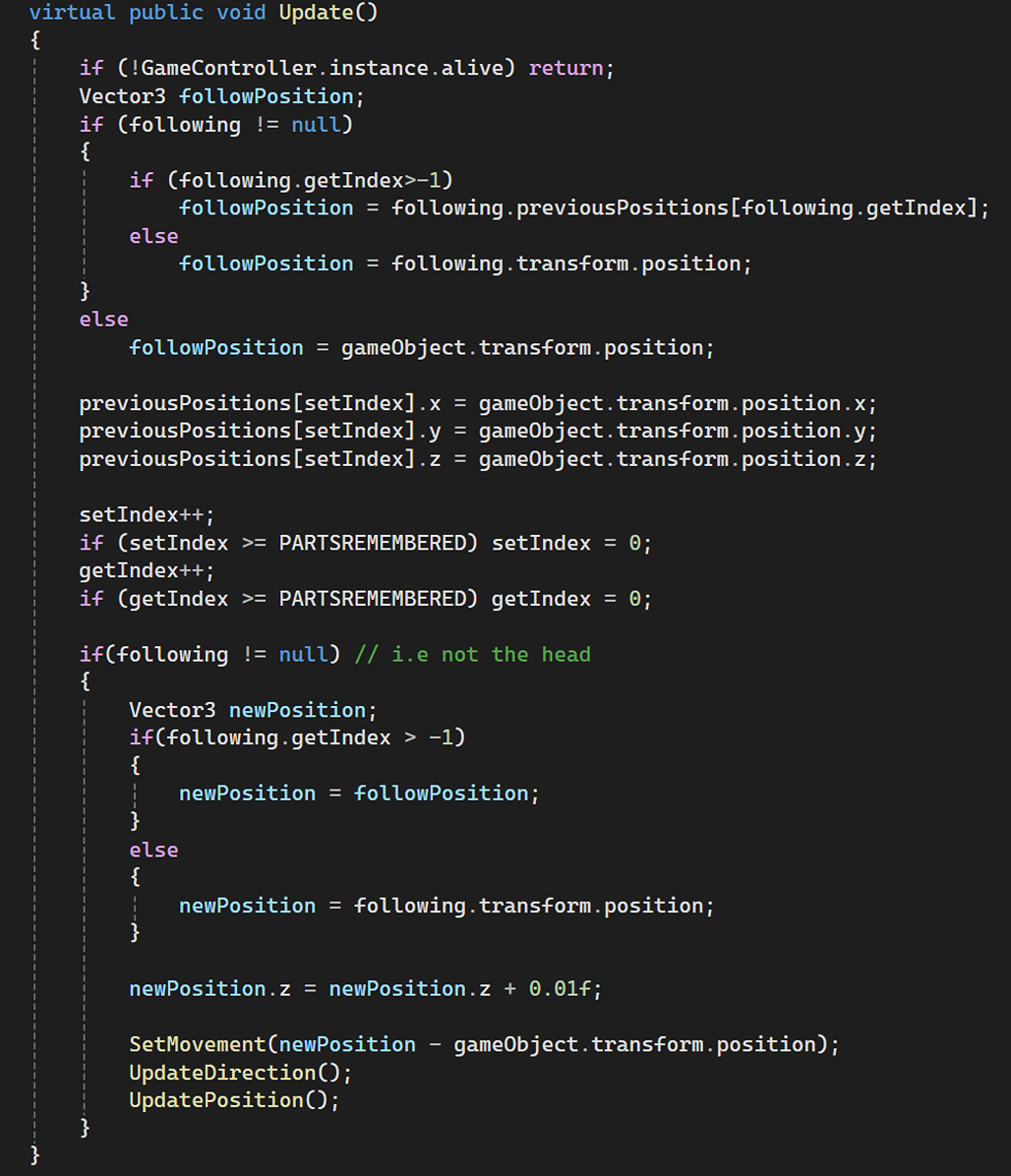
Audio Management
Playing different audio clips in response to game events like eating an egg or dying.
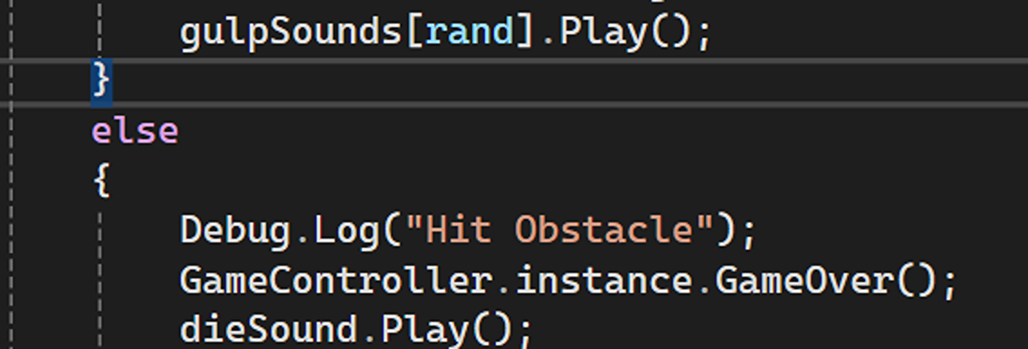
Sprite Manipulation
Changing sprite visuals dynamically, for example, changing body parts to a tail or body.
![]()
Randomization
Using random values to generate the positions, rotations, and scales of objects like eggs, spikes, and rocks.
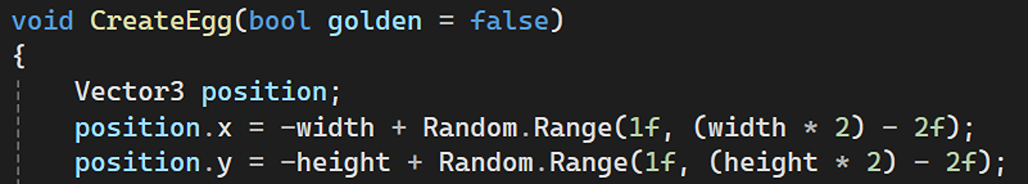
Memory Management
Managing the positions of objects over time (e.g., snake body parts remembering past positions).
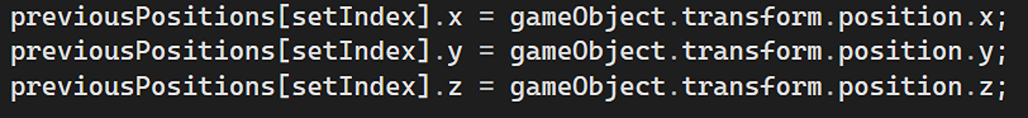
Game Over Logic and Restart
Handling the game-over logic, resetting the snake, and restarting the game with updated stats.